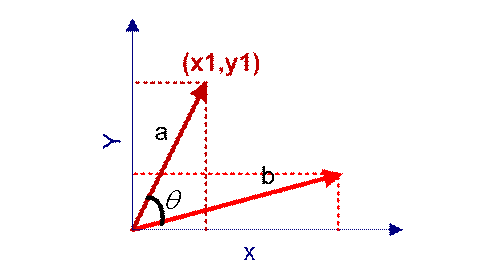
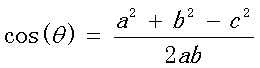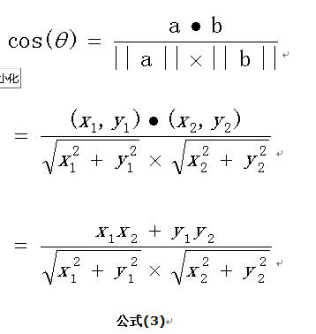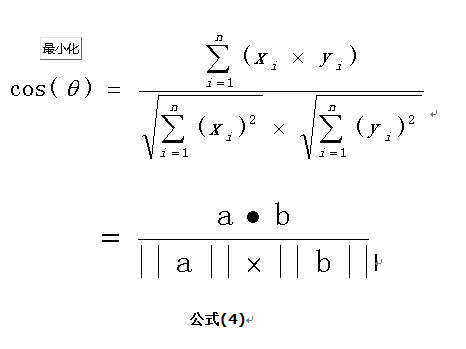余弦相似度用向量空间中两个向量夹角的余弦值作为衡量两个个体间差异的大小。余弦值越接近 1,就表明夹角越接近 0 度,也就是两个向量越相似,这就叫”余弦相似性”。
我们知道,对于两个向量,如果他们之间的夹角越小,那么我们认为这两个向量是越相似的。余弦相似性就是利用了这个理论思想。它通过计算两个向量的夹角的余弦值来衡量向量之间的相似度值。余弦相似性推导公式如下:
public class Cosine {public static double getSimilarity(String doc1, String doc2) {if (doc1 != null && doc1.trim().length() > 0 && doc2 != null&& doc2.trim().length() > 0) {Map<Integer, int[]> AlgorithmMap = new HashMap<Integer, int[]>();
// 将两个字符串中的中文字符以及出现的总数封装到,AlgorithmMap 中
for (int i = 0; i < doc1.length(); i++) {char d1 = doc1.charAt(i);
if(isHanZi(d1)){// 标点和数字不处理
int charIndex = getGB2312Id(d1);// 保存字符对应的 GB2312 编码
if(charIndex != -1){int[] fq = AlgorithmMap.get(charIndex);
if(fq != null && fq.length == 2){fq[0]++;// 已有该字符,加 1
}else {fq = new int[2];
fq[0] = 1;
fq[1] = 0;
AlgorithmMap.put(charIndex, fq);// 新增字符入 map
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < doc2.length(); i++) {char d2 = doc2.charAt(i);
if(isHanZi(d2)){int charIndex = getGB2312Id(d2);
if(charIndex != -1){int[] fq = AlgorithmMap.get(charIndex);
if(fq != null && fq.length == 2){fq[1]++;
}else {fq = new int[2];
fq[0] = 0;
fq[1] = 1;
AlgorithmMap.put(charIndex, fq);
}
}
}
}
Iterator<Integer> iterator = AlgorithmMap.keySet().iterator();
double sqdoc1 = 0;
double sqdoc2 = 0;
double denominator = 0;
while(iterator.hasNext()){int[] c = AlgorithmMap.get(iterator.next());
denominator += c[0]*c[1];
sqdoc1 += c[0]*c[0];
sqdoc2 += c[1]*c[1];
}
return denominator / Math.sqrt(sqdoc1*sqdoc2);// 余弦计算
} else {throw new NullPointerException(" the Document is null or have not cahrs!!");
}
}
public static boolean isHanZi(char ch) {
// 判断是否汉字
return (ch >= 0x4E00 && ch <= 0x9FA5);
/*if (ch >= 0x4E00 && ch <= 0x9FA5) {// 汉字
return true;
}else{
String str = "" + ch;
boolean isNum = str.matches("[0-9]+");
return isNum;
}*/
/*if(Character.isLetterOrDigit(ch)){
String str = "" + ch;
if (str.matches("[0-9a-zA-Z\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]+")){// 非乱码
return true;
}else return false;
}else return false;*/
}
/**
* 根据输入的 Unicode 字符,获取它的 GB2312 编码或者 ascii 编码,
*
* @param ch 输入的 GB2312 中文字符或者 ASCII 字符 (128 个)
* @return ch 在 GB2312 中的位置,- 1 表示该字符不认识
*/
public static short getGB2312Id(char ch) {
try {byte[] buffer = Character.toString(ch).getBytes("GB2312");
if (buffer.length != 2) {
// 正常情况下 buffer 应该是两个字节,否则说明 ch 不属于 GB2312 编码,故返回 '?',此时说明不认识该字符
return -1;
}
int b0 = (int) (buffer[0] & 0x0FF) - 161; // 编码从 A1 开始,因此减去 0xA1=161
int b1 = (int) (buffer[1] & 0x0FF) - 161;
return (short) (b0 * 94 + b1);// 第一个字符和最后一个字符没有汉字,因此每个区只收 16*6-2=94 个汉字
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1=" 担保人姓名 ";
String str2=" 个人法定名称 ";
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
double Similarity=Cosine.getSimilarity(str1, str2);
System.out.println(" 用时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start));
System.out.println(Similarity);
}
}